Resource Center
纳米发电机™纳米粒子合成系统
.png)
PreciGenome NanoGenerator™ 是用于纳米粒子合成的高性能仪器,如脂质纳米粒子、脂质体、PLGA 等,广泛用于药物输送、基因治疗、LNP 配制和制造等。
NanoGenerator™ 生成的纳米粒子具有更好的尺寸均匀性和更小的 PDI。它可从 0.1mL/样品筛选扩展到 1L(>10L 定制设计)大批量 GMP 生产
纳米粒子,尤其是脂质体和聚合物纳米粒子,由于其优异的性能,在药物递送、mRNA疫苗和生物传感等制药工业等各个领域显示出巨大的生物医学应用潜力。
通过微流控技术合成纳米颗粒比传统的批量合成工艺具有优势,因为它能够在尺寸和形状上具有更好的均匀性。例如,在药物递送领域,使用NanoGenerator™纳米粒子合成系统可以合成脂质纳米粒子(LNP)、脂质体、PLGA等多种纳米粒子。脂质纳米颗粒 (LNP)、脂质体和 PLGA 是最常用的可生物降解材料,用于输送亲水性和疏水性化合物。
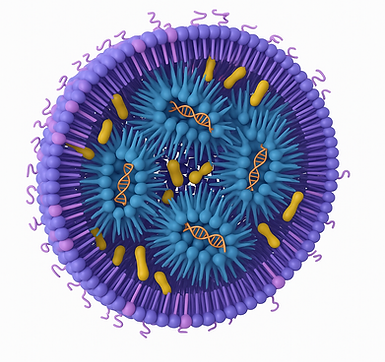
Lipid Nanoparticles are a class of nanoscale delivery systems designed to transport and protect therapeutic molecules, such as drugs and RNA, to specific target sites within the body. They have gained significant attention in the field of medicine and biotechnology due to their ability to enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of drugs by improving stability and ability to target points of interest for drug delivery.
The basic structure of an LNP consists of a lipid bilayer surrounding a hydrophobic core. This structure allows the LNPs to encapsulate hydrophobic drugs or nucleic acids within the core while keeping the hydrophilic components on the surface, making them stable and compatible with the aqueous environment of the body.

Modern LNPs comprise four essential components: cationic/ionizable lipid, helper lipid, cholesterol and PEGylated lipid. Each serves specific functions in the delivery system.
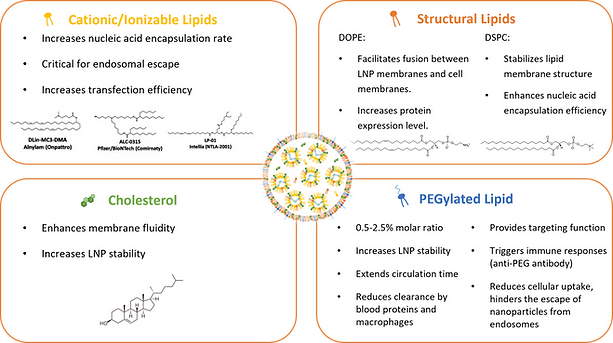
Essential components of LNPs
LNP Introduction
粒子合成原理:
Conventionally, solvent injection and thin film rehydration are two common methods for liposome synthesis. Due to the simplicity of equipment requirements, such as sonicators or rotary evaporators, solvent injection and thin film rehydration methods are widely adopted in both research and production process. However, these traditional methods meet the challenges of low homogeneity of resulted LNPs, hash processes for delicate biomolecules, such as DNAs, RNAs or proteins.
Overview of LNP Synthesis, Formulation and Manufacturing Methods
This report reviews the various traditional approaches to LNP synthesis, contrasts them with microfluidic synthesis, and provides an overview of key synthesis parameters and downstream processing methods. While several traditional manufacturing methods have laid the foundation for current LNP technologies, modern methods use microfluidics for superior precision, reproducibility, and scalability.
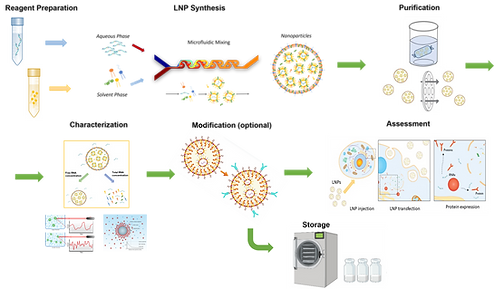
Introduction to Lipid Nanoparticle: LNP Formulation Design and Preparation
This technical introduction explores lipid nanoparticle types, the formulation design, and preparation workflow of LNPs, highlighting common types, their typical composition, supported cargoes, and basic preparation considerations.
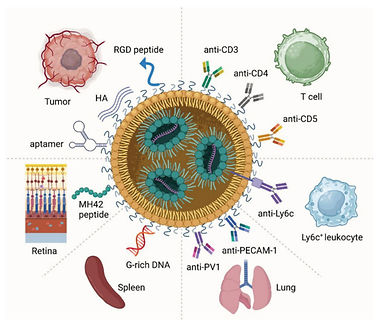
Targeted Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticles Through Surface Modification
This report explains the structural basis of LNP targeting, passive and active targeting mechanisms, and cutting-edge surface engineering techniques. Surface modifications— ranging from ligand conjugation to advanced lipid engineering — play a critical role in overcoming biological barriers, enhancing cellular uptake, and directing LNPs to specific tissues or cell populations.
To address these challenges, microfluidic mixing method has been rapidly developed in the past decade.
Small volume(0.1-0.5 ml) lipid nanoparticle preparation for drug discovery and screening
LNP formulation tutorial with 1-4 samples per run
Automated high throughput screening LNP platform
Media volume(1- 200 ml) lipid nanoparticle process for formulation development and optimization, candidate selection in the pre-clinical study
Large volume (>100mL) lipid nanoparticle process for clinical development, GMP manufacturing.
有效载荷:
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are versatile carriers that protect and deliver a wide spectrum of therapeutic payloads across nucleic acids, proteins, peptides, and small molecules.
Below is a concise overview of commonly used LNP cargos and what they enable.
-
Linear mRNA: Encodes transient protein expression with high potency and rapid onset, widely used for vaccines and protein replacement.
-
Circular mRNA (circRNA): Covalently closed RNAs that resist exonuclease degradation and support more durable expression with reduced innate sensing.
-
Self-amplifying RNA (saRNA): Incorporates replicase to amplify intracellularly, achieving higher, longer expression at lower doses, with formulation tuned for larger genomes.
-
siRNA: Double-stranded silencers that trigger RNA interference for gene knockdown, validated clinically and enabled by efficient endosomal escape.
-
DNA (plasmid/ssDNA): Supports longer-term, promoter-controlled expression and larger cargos, requiring strategies to manage innate immune activation.
-
Guide RNA (gRNA): Delivered alone or with Cas mRNA/RNP to program CRISPR editing; co-formulation supports precise, transient genome modification.
-
Peptides: Therapeutic, targeting, or immunomodulatory sequences; amphiphilic design and ion pairing improve encapsulation, stability, and intracellular delivery.
-
Proteins: Enzymes, antibodies, and genome-editing nucleases delivered via electrostatic complexation or anionic-lipid strategies while preserving bioactivity.
-
Small molecules: Hydrophobic or hydrophilic drugs formulated to enhance solubility, stability, bioavailability, tissue distribution, and controlled release.

mRNA

guide RNA

Protein

Circular RNA (circRNA)

DNA

Small Molecule
Across these payloads, LNP composition is tailored—ionizable lipid for complexation and endosomal escape, helper phospholipid and cholesterol for structure and fusion, and PEG-lipid for colloidal stability and biodistribution. Microfluidic mixing, pKa tuning, particle size control, and surface ligands further optimize encapsulation efficiency, potency, tissue selectivity, and safety. Together, these design levers make LNPs a unifying platform for vaccines, gene regulation, genome editing, protein delivery, and small-molecule therapeutics.
合成系统应用:
Gene Therapy
Genetic drugs, including small interfering RNA (siRNA), mRNA, or plasmid DNA, hold promise for treating a wide array of diseases by either suppressing harmful genes, producing therapeutic proteins, or employing gene-editing techniques. Currently, lipid nanoparticle (LNP) systems stand at the forefront among non-viral delivery methods, enabling the clinical utilization of genetic drugs.
Immunotherapy

Immunotherapy entails the transformation of cells, commonly immune cells, obtained either from the patient (autologous) or a compatible donor (allogeneic). These modified cells undergo isolation, amplification, and are later reintroduced into the patient. Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) present a versatile approach to cell reprogramming, facilitating the transfer of RNA responsible for protein expression or gene editing.
Vaccines

Lipid nanoparticle has played a pivotal role in expediting the development of vaccines, as demonstrated by Pfizer and Moderna in the COVID-19 pandemic response. It allows for precise and high-throughput screening of potential vaccine candidates. The technology facilitates rapid testing, antigen formulation, and optimization of vaccine delivery systems.
Other Areas

Other applications including cosmetics, medical imaging, nutrition, agrochemicals, etc.
The cosmetics sector stood at the forefront in acknowledging and utilizing nanotechnology advancements in diverse product innovations. Liposomal cosmetic formulations are expected to offer several benefits, including improved stability and effectiveness, along with successful ingredient penetration into the skin. A variety of liposomal cosmetics are currently in use.
演示视频和网络研讨会:
纳米发电机™ProMab Biotechnologies 的 LNP 合成与应用网络研讨会
Lipid nanoparticle LNP application in gene editing, CRISPR-Cas9
应用注意事项:
应用注意事项:
应用注意事项:
Lipid Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Advances